模型权重
几种模型权重:
输入模版及 tokenizer
LLaVA 使用 LLM 的 Instruction 模版为基础, 使用 <image> 作为图像的 token, 作为 user message 的一部分, 整合到模版中. 以 liuhaotian/llava-v1.6-mistral-7b 为例, Mistral 系列的 Instruction 如下:
1
| <s> [INST] Instruction [/INST] Model answer</s> [INST] Follow-up instruction [/INST]
|
引入图像后, LLaVA 使用如下的代码拼接图像和文本:
1
2
3
4
5
| # DEFAULT_IMAGE_TOKEN = <image>
if model.config.mm_use_im_start_end:
inp = DEFAULT_IM_START_TOKEN + DEFAULT_IMAGE_TOKEN + DEFAULT_IM_END_TOKEN + '\n' + inp
else:
inp = DEFAULT_IMAGE_TOKEN + '\n' + inp
|
最终得到的输入 prompt 如下:
1
| [INST] <image>\nIs there any person in this photo [/INST]
|
对于多轮对话, 图像只在 prompt 中出现一次. 也就是说只有第一轮拼接了图像的 token, 之后的轮次, 按照模版扩展. 一个两轮对话的例子:
1
2
| [INST] <image>
Is there any person in this photo [/INST] <s> No, there is no person visible in the photo. The image shows a wooden dock extending into a calm body of water, with a mountainous landscape in the background. The focus is on the dock and the serene natural setting. </s> </s>[INST] Give me all texts in this photo [/INST]
|
总之, LLaVA 的 tokenizer 通过增加 <image> 特殊字符作为图片的占位符, 有几张图片, 就要在 prompt 中有相应数量的 <image> 占位符.
模型结构
目前 LLaVA 有 v1, v1.5, v1.6 几个版本, 不同版本之间的结构相同, 区别在于使用的 LLM 模型, 以及训练方法的不同, 模型列表可以参考 Model Zoo. 这里一并介绍其模型结构.

LLaVA 主要有三部分组成: Pre-trained LLM, Pre-trained Vision Encoder, Projection Layers.
Pre-trained Vision Encoder 和 Projection Layers: 使用预训练的 CLIP-ViT-L/14 作为 vision encoder. 将输入的 image 表征为 $Z_{v}$, 再经过一个线性层 Projection Layers, 将 vision encoder 的编码 $Z_{v}$ 的维度转化为与 LLM embedding 空间相同的维度的表征 $H_{v}$, 从而可以作为 LLM 的输入.
Pre-trained LLM 选用的模型为 LLaMA2, Mistral, Vicuna, Yi 等系列的模型.
Forward 的过程是将文本 instruction prompt 通过 LLM 的 embedding 层, 得到文本 token 的表征 $H_{q}$, 然后将文本的表征序列与和图像的表征序列, 在序列维度上按特定的模版 concatnate 在一起, 得到新的更长的序列, 将这个序列输入到 LLM 进行生成.
模型输入
这里指的是输入到 LLM 的 embeddings 矩阵是怎么构成的. 关键是序列中 <image> 图片占位符, 要怎么拼接到 embeddings 中.
先说结果, 一张图片会先被切分为多个 patches, 然后和 resize 到相同维度的原始图片 concat 在一起, 传入到 Vision Encoder 得到每个像素的表征, 并进行 flatten, 将 patches, weight, height 都碾平到序列的样式, 形成 (像素总数量, 表征维度) 这样的尺寸, 然后作为图片的表征序列, 融合到文本序列中.
比如 [INST] <image>\nIs there any person in this photo [/INST] 这个 prompt, <image> 前面部分 [INST] 有 5 个 tokens, 后面部分 \nIs there any person in this photo [/INST] 有 25 个 tokens, 被转换后的图像有 2700 个像素, 最终按 5 + 2700 + 25 的顺序组成一个长度为 2730 的 input_embed, 作为模型的输入.
这是其中一张图片的处理方法, 如果输入有多张图片, 将每张图片的像素表征序列插入到对应的 <image> 图片占位符位置, 形成最终的长序列.
可以看到, 图像占据了输入的绝大部分位置, 这是由于按像素表征, 还划分了 patches, 使得像素量远远大于文本 tokens 的数量.
相关代码.
处理图像
根据原始输入图像的分辨率, 将图像 resize 到最合适的尺寸, 然后按固定的大小切分为若干个 patches. 将原始图片也 resize 到 patch 的尺寸, 然后将原始图片和切分的 patches 合并在一起, 并且原始图片放在第一位.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| def process_images(images, image_processor, model_cfg):
image_aspect_ratio = getattr(model_cfg, "image_aspect_ratio", None)
new_images = []
if image_aspect_ratio == 'pad':
for image in images:
image = expand2square(image, tuple(int(x*255) for x in image_processor.image_mean))
image = image_processor.preprocess(image, return_tensors='pt')['pixel_values'][0]
new_images.append(image)
elif image_aspect_ratio == "anyres":
for image in images:
image = process_anyres_image(image, image_processor, model_cfg.image_grid_pinpoints) # 走这里
new_images.append(image)
else:
return image_processor(images, return_tensors='pt')['pixel_values']
if all(x.shape == new_images[0].shape for x in new_images):
new_images = torch.stack(new_images, dim=0)
return new_images
def process_anyres_image(image, processor, grid_pinpoints):
"""
Process an image with variable resolutions.
Args: image (PIL.Image.Image): The input image to be processed. processor: The image processor object. grid_pinpoints (str): A string representation of a list of possible resolutions.
Returns: torch.Tensor: A tensor containing the processed image patches. """ if type(grid_pinpoints) is list:
possible_resolutions = grid_pinpoints
else:
possible_resolutions = ast.literal_eval(grid_pinpoints)
best_resolution = select_best_resolution(image.size, possible_resolutions) # 选择最优的 resize 分辨率
image_padded = resize_and_pad_image(image, best_resolution) # resize 操作, 并进行 pad 操作
patches = divide_to_patches(image_padded, processor.crop_size['height']) # 将图像按固定的数值, 切分为多个 patches
image_original_resize = image.resize((processor.size['shortest_edge'], processor.size['shortest_edge'])) # 将原始图片也 resize 到 patch 的尺寸
image_patches = [image_original_resize] + patches
image_patches = [processor.preprocess(image_patch, return_tensors='pt')['pixel_values'][0]
for image_patch in image_patches] # 将原始图片和切分的 patches 合并在一起, 并且原始图片放在第一位
return torch.stack(image_patches, dim=0)
|
进行 tokenize
将带有图片占位符的文本序列进行 tokenize, 得到 input_ids. 这里图片占位符只占一个 token, 对应的 token id 为 IMAGE_TOKEN_INDEX(-200).
注意这里的 input_ids 不会直接丢给模型的 forward(训练) 或 generate(推理), 作用是引导图文的 embedding 融合得到 input_embed, 作为模型的输入.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| def tokenizer_image_token(prompt, tokenizer, image_token_index=IMAGE_TOKEN_INDEX, return_tensors=None):
prompt_chunks = [tokenizer(chunk).input_ids for chunk in prompt.split('<image>')]
def insert_separator(X, sep):
return [ele for sublist in zip(X, [sep]*len(X)) for ele in sublist][:-1]
input_ids = []
offset = 0
if len(prompt_chunks) > 0 and len(prompt_chunks[0]) > 0 and prompt_chunks[0][0] == tokenizer.bos_token_id:
offset = 1
input_ids.append(prompt_chunks[0][0])
for x in insert_separator(prompt_chunks, [image_token_index] * (offset + 1)):
input_ids.extend(x[offset:])
if return_tensors is not None:
if return_tensors == 'pt':
return torch.tensor(input_ids, dtype=torch.long)
raise ValueError(f'Unsupported tensor type: {return_tensors}')
return input_ids
|
根据 tokenizer 得到的 input_ids 转化为 input_embed
以 forward() 函数为例.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| def forward(
self,
input_ids: torch.LongTensor = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[List[torch.FloatTensor]] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
labels: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
use_cache: Optional[bool] = None,
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None,
output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None,
images: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
image_sizes: Optional[List[List[int]]] = None,
return_dict: Optional[bool] = None,
) -> Union[Tuple, CausalLMOutputWithPast]:
if inputs_embeds is None:
(
input_ids,
position_ids,
attention_mask,
past_key_values,
inputs_embeds,
labels
) = self.prepare_inputs_labels_for_multimodal(
input_ids,
position_ids,
attention_mask,
past_key_values,
labels,
images,
image_sizes
)
return super().forward(
input_ids=input_ids, # 这里的 input_ids 为 None
attention_mask=attention_mask,
position_ids=position_ids,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds, # 融合了文本图像表征, 组成的序列表征
labels=labels,
use_cache=use_cache,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,
return_dict=return_dict
)
|
合并的逻辑很复杂, 如下.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
| def prepare_inputs_labels_for_multimodal(
self, input_ids, position_ids, attention_mask, past_key_values, labels,
images, image_sizes=None
):
vision_tower = self.get_vision_tower()
if vision_tower is None or images is None or input_ids.shape[1] == 1:
return input_ids, position_ids, attention_mask, past_key_values, None, labels
if type(images) is list or images.ndim == 5:
if type(images) is list:
images = [x.unsqueeze(0) if x.ndim == 3 else x for x in images]
concat_images = torch.cat([image for image in images], dim=0)
image_features = self.encode_images(concat_images)
split_sizes = [image.shape[0] for image in images]
image_features = torch.split(image_features, split_sizes, dim=0)
mm_patch_merge_type = getattr(self.config, 'mm_patch_merge_type', 'flat')
image_aspect_ratio = getattr(self.config, 'image_aspect_ratio', 'square')
if mm_patch_merge_type == 'flat':
image_features = [x.flatten(0, 1) for x in image_features]
elif mm_patch_merge_type.startswith('spatial'):
new_image_features = []
for image_idx, image_feature in enumerate(image_features):
if image_feature.shape[0] > 1:
base_image_feature = image_feature[0]
image_feature = image_feature[1:]
height = width = self.get_vision_tower().num_patches_per_side
assert height * width == base_image_feature.shape[0]
if image_aspect_ratio == 'anyres':
num_patch_width, num_patch_height = get_anyres_image_grid_shape(image_sizes[image_idx], self.config.image_grid_pinpoints, self.get_vision_tower().config.image_size)
image_feature = image_feature.view(num_patch_height, num_patch_width, height, width, -1)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
if 'unpad' in mm_patch_merge_type:
image_feature = image_feature.permute(4, 0, 2, 1, 3).contiguous()
image_feature = image_feature.flatten(1, 2).flatten(2, 3)
image_feature = unpad_image(image_feature, image_sizes[image_idx])
image_feature = torch.cat((
image_feature,
self.model.image_newline[:, None, None].expand(*image_feature.shape[:-1], 1).to(image_feature.device)
), dim=-1)
image_feature = image_feature.flatten(1, 2).transpose(0, 1)
else:
image_feature = image_feature.permute(0, 2, 1, 3, 4).contiguous()
image_feature = image_feature.flatten(0, 3)
image_feature = torch.cat((base_image_feature, image_feature), dim=0)
else:
image_feature = image_feature[0]
if 'unpad' in mm_patch_merge_type:
image_feature = torch.cat((
image_feature,
self.model.image_newline[None].to(image_feature.device)
), dim=0)
new_image_features.append(image_feature)
image_features = new_image_features
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unexpected mm_patch_merge_type: {self.config.mm_patch_merge_type}")
else:
image_features = self.encode_images(images)
# TODO: image start / end is not implemented here to support pretraining.
if getattr(self.config, 'tune_mm_mlp_adapter', False) and getattr(self.config, 'mm_use_im_start_end', False):
raise NotImplementedError
# Let's just add dummy tensors if they do not exist,
# it is a headache to deal with None all the time. # But it is not ideal, and if you have a better idea, # please open an issue / submit a PR, thanks. _labels = labels
_position_ids = position_ids
_attention_mask = attention_mask
if attention_mask is None:
attention_mask = torch.ones_like(input_ids, dtype=torch.bool)
else:
attention_mask = attention_mask.bool()
if position_ids is None:
position_ids = torch.arange(0, input_ids.shape[1], dtype=torch.long, device=input_ids.device)
if labels is None:
labels = torch.full_like(input_ids, IGNORE_INDEX)
# remove the padding using attention_mask -- FIXME
_input_ids = input_ids
input_ids = [cur_input_ids[cur_attention_mask] for cur_input_ids, cur_attention_mask in zip(input_ids, attention_mask)]
labels = [cur_labels[cur_attention_mask] for cur_labels, cur_attention_mask in zip(labels, attention_mask)]
new_input_embeds = []
new_labels = []
cur_image_idx = 0
for batch_idx, cur_input_ids in enumerate(input_ids):
num_images = (cur_input_ids == IMAGE_TOKEN_INDEX).sum()
if num_images == 0:
cur_image_features = image_features[cur_image_idx]
cur_input_embeds_1 = self.get_model().embed_tokens(cur_input_ids)
cur_input_embeds = torch.cat([cur_input_embeds_1, cur_image_features[0:0]], dim=0)
new_input_embeds.append(cur_input_embeds)
new_labels.append(labels[batch_idx])
cur_image_idx += 1
continue
image_token_indices = [-1] + torch.where(cur_input_ids == IMAGE_TOKEN_INDEX)[0].tolist() + [cur_input_ids.shape[0]]
cur_input_ids_noim = []
cur_labels = labels[batch_idx]
cur_labels_noim = []
for i in range(len(image_token_indices) - 1):
cur_input_ids_noim.append(cur_input_ids[image_token_indices[i]+1:image_token_indices[i+1]])
cur_labels_noim.append(cur_labels[image_token_indices[i]+1:image_token_indices[i+1]])
split_sizes = [x.shape[0] for x in cur_labels_noim]
cur_input_embeds = self.get_model().embed_tokens(torch.cat(cur_input_ids_noim))
cur_input_embeds_no_im = torch.split(cur_input_embeds, split_sizes, dim=0)
cur_new_input_embeds = []
cur_new_labels = []
for i in range(num_images + 1):
cur_new_input_embeds.append(cur_input_embeds_no_im[i])
cur_new_labels.append(cur_labels_noim[i])
if i < num_images:
cur_image_features = image_features[cur_image_idx]
cur_image_idx += 1
cur_new_input_embeds.append(cur_image_features)
cur_new_labels.append(torch.full((cur_image_features.shape[0],), IGNORE_INDEX, device=cur_labels.device, dtype=cur_labels.dtype))
cur_new_input_embeds = [x.to(self.device) for x in cur_new_input_embeds]
cur_new_input_embeds = torch.cat(cur_new_input_embeds)
cur_new_labels = torch.cat(cur_new_labels)
new_input_embeds.append(cur_new_input_embeds)
new_labels.append(cur_new_labels)
# Truncate sequences to max length as image embeddings can make the sequence longer
tokenizer_model_max_length = getattr(self.config, 'tokenizer_model_max_length', None)
if tokenizer_model_max_length is not None:
new_input_embeds = [x[:tokenizer_model_max_length] for x in new_input_embeds]
new_labels = [x[:tokenizer_model_max_length] for x in new_labels]
# Combine them
max_len = max(x.shape[0] for x in new_input_embeds)
batch_size = len(new_input_embeds)
new_input_embeds_padded = []
new_labels_padded = torch.full((batch_size, max_len), IGNORE_INDEX, dtype=new_labels[0].dtype, device=new_labels[0].device)
attention_mask = torch.zeros((batch_size, max_len), dtype=attention_mask.dtype, device=attention_mask.device)
position_ids = torch.zeros((batch_size, max_len), dtype=position_ids.dtype, device=position_ids.device)
for i, (cur_new_embed, cur_new_labels) in enumerate(zip(new_input_embeds, new_labels)):
cur_len = cur_new_embed.shape[0]
if getattr(self.config, 'tokenizer_padding_side', 'right') == "left":
new_input_embeds_padded.append(torch.cat((
torch.zeros((max_len - cur_len, cur_new_embed.shape[1]), dtype=cur_new_embed.dtype, device=cur_new_embed.device),
cur_new_embed
), dim=0))
if cur_len > 0:
new_labels_padded[i, -cur_len:] = cur_new_labels
attention_mask[i, -cur_len:] = True
position_ids[i, -cur_len:] = torch.arange(0, cur_len, dtype=position_ids.dtype, device=position_ids.device)
else:
new_input_embeds_padded.append(torch.cat((
cur_new_embed,
torch.zeros((max_len - cur_len, cur_new_embed.shape[1]), dtype=cur_new_embed.dtype, device=cur_new_embed.device)
), dim=0))
if cur_len > 0:
new_labels_padded[i, :cur_len] = cur_new_labels
attention_mask[i, :cur_len] = True
position_ids[i, :cur_len] = torch.arange(0, cur_len, dtype=position_ids.dtype, device=position_ids.device)
new_input_embeds = torch.stack(new_input_embeds_padded, dim=0)
if _labels is None:
new_labels = None
else:
new_labels = new_labels_padded
if _attention_mask is None:
attention_mask = None
else:
attention_mask = attention_mask.to(dtype=_attention_mask.dtype)
if _position_ids is None:
position_ids = None
return None, position_ids, attention_mask, past_key_values, new_input_embeds, new_labels
|
训练过程
LLaVA 的训练包含两个阶段, 预训练和微调.
预训练
预训练阶段是在 Image-Text Pair 数据集上进行的, 形式上是单轮训练. 从CC3M数据中过滤了595K Image-Text Pairs, 训练过程中, 只训练 Projection layers 中的参数, LLM 和 vision encoder 是冻结住的. 具体来说, CC3M 只包含了图像文本对, 可以看做是 (image, caption), 论文中使用 GPT-4 生成了一些多样化的 Instruction, 将简单的图像文本对扩展成了 (image, instruction, caption) 这种形式的三元组. 下图是生成的一些 instructions.

预训练这个阶段是为了训练一个较好的 projection layer 可以将 visual feature 映射到 linguistic space, 也就是为了让 vision encoder 和 LLM 实现对齐.
这个阶段结束之后模型获得了一个初步的理解图像的能力.
微调阶段
微调阶段只冻结 vision encoder 中的参数, LLM 和 Projection layers 会放开训练. 这一阶段的目的是为了让模型更好地遵循用户给出的 Instruction.
这个阶段分为两种任务: 多轮形式的 Instruct Tuning 和单轮形式的 Science QA 上的问答.
微调阶段的模版如下, 这是多轮形式的, 如果样本是单轮任务, 只需要有一组 user-assistant pair. 其中计算损失的 token 是下图中的绿色序列和 tokens, 也就是说训练模型来预测模型的回答以及在哪里停止输出.

以符号表示, 多轮形式的样本可以表示为, 其中 $T$ 代表了对话的轮次, $q$ 代表 user 轮次的文本输入, $a$ 代表模型回答轮次:
$$
\left(\mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{q}}^1, \mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{a}}^1, \cdots, \mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{q}}^T, \mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{a}}^T\right)
$$
上面 $X_{q}^{t}$ 代表的文本部分, 图片部分 $X_v$ 只在第一轮融入, 将文本和图像随机选择一种前后关系拼接在一起, 作为完整的 instruct.
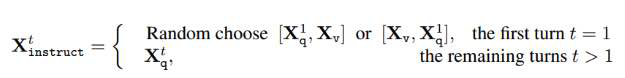
微调阶段的数据也是由 GPT-4 生成的. 由于 GPT-4 是纯文本输入, 所以要使用 GPT-4 来生成一些针对图片的问题和答案就需要将图片表示成GPT-4可以理解的形式.
对于一张图片, 论文中用 5 句 caption 以及图片中 object 的 bounding box 的坐标数值来表示一张图片, 然后通过设计特定的 prompt 以及一些 examples, 让 GPT-4 生成针对一张图片的 conversation, detailed description, complex reasoning 三种类型的数据.

参考资料
![]()
![]()
![]()
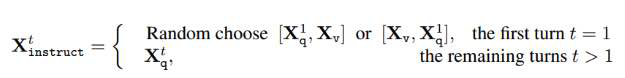
![]()